How Do You Know if a Molecule Is Symmetrical
4.12: Shapes and Properties- Polar and Nonpolar Molecules
- Page ID
- 351234
Learning Objective
- Determine if a molecule is polar or nonpolar.
Molecular Polarity
To determine if a molecule is polar or nonpolar, it is ofttimes useful to look at Lewis structures. Nonpolar compounds will exist symmetric, meaning all of the sides around the central atom are identical - bonded to the aforementioned element with no unshared pairs of electrons. Notice that a tetrahedral molecule such as \(\ce{CCl_4}\) is nonpolar Effigy (\(\PageIndex{1}\). Another non polar molecule shown below is boron trifluoride, BFthree. BFiii is a trigonal planar molecule and all three peripheral atoms are the same.

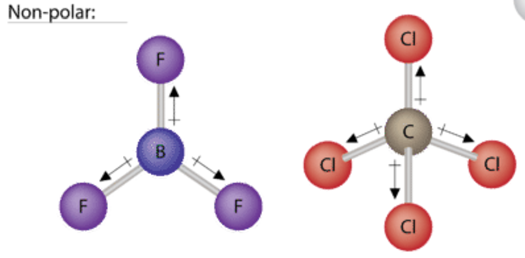

Polar molecules are disproportionate, either containing lone pairs of electrons on a key cantlet or having atoms with different electronegativities bonded. This works pretty well - as long equally y'all can visualize the molecular geometry. That's the hard part. To know how the bonds are oriented in space, yous take to have a stiff grasp of Lewis structures and VSEPR theory. Assuming you do, you can expect at the structure of each one and determine if it is polar or not - whether or not y'all know the individual cantlet electronegativity. This is because you know that all bonds between dissimilar elements are polar, and in these particular examples, it doesn't matter which direction the dipole moment vectors are pointing (out or in).
A polar molecule is a molecule in which one finish of the molecule is slightly positive, while the other stop is slightly negative. A diatomic molecule that consists of a polar covalent bail, such equally \(\ce{HF}\), is a polar molecule.
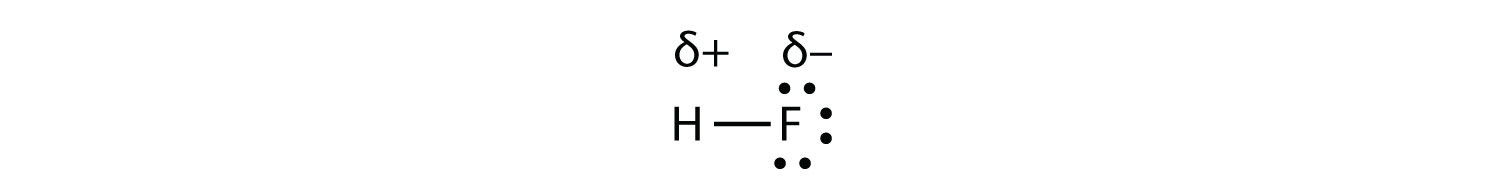
Every bit mentioned in section 4.7, because the electrons in the bail are nearer to the F cantlet, this side of the molecule takes on a partial negative charge, which is represented past δ− (δ is the lowercase Greek letter delta). The other side of the molecule, the H cantlet, adopts a partial positive charge, which is represented by δ+. The 2 electrically charged regions on either end of the molecule are called poles, similar to a magnet having a north and a south pole. A molecule with ii poles is called a dipole (see figure below). Hydrogen fluoride is a dipole.

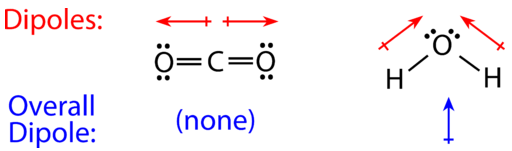
For molecules with more than two atoms, the molecular geometry must besides be taken into account when determining if the molecule is polar or nonpolar. The effigy beneath shows a comparing between carbon dioxide and h2o. Carbon dioxide \(\left( \ce{CO_2} \right)\) is a linear molecule. The oxygen atoms are more than electronegative than the carbon atom, so there are two private dipoles pointing outward from the \(\ce{C}\) atom to each \(\ce{O}\) atom. However, since the dipoles are of equal force and are oriented this mode, they abolish out and the overall molecular polarity of \(\ce{CO_2}\) is nil.
Water is a aptitude molecule considering of the ii lone pairs on the central oxygen cantlet. The individual dipoles indicate from the \(\ce{H}\) atoms toward the \(\ce{O}\) cantlet. Because of the shape, the dipoles do not cancel each other out and the h2o molecule is polar. In the figure beneath, the cyberspace dipole is shown in blue and points upward.
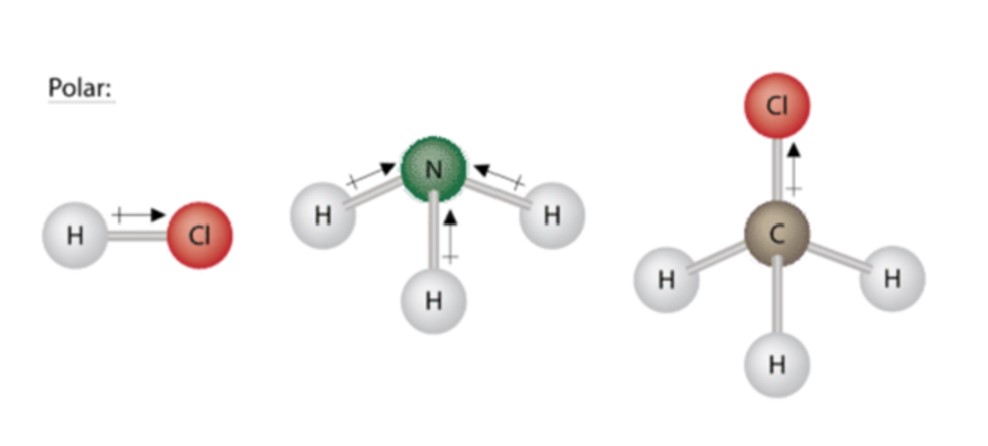
Three other polar molecules are shown beneath with the arrows pointing to the more than electron dense atoms. Just like the water molecule, none of the bond moments cancel out.
To summarize, to be polar, a molecule must:
- Contain at to the lowest degree 1 polar covalent bond.
- Take a molecular structure such that the sum of the vectors of each bond dipole moment does not abolish.
Steps to Identify Polar Molecules
- Describe the Lewis construction
- Effigy out the geometry (using VSEPR theory)
- Visualize or draw the geometry
- Find the net dipole moment (you lot don't take to actually do calculations if you can visualize it)
- If the net dipole moment is goose egg, it is not-polar. Otherwise, it is polar.
Example \(\PageIndex{i}\):
Label each of the following as polar or nonpolar.
- Water, H2O:
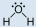
- Methanol, CHthreeOH:
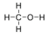
- Hydrogen Cyanide, HCN:
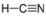
- Oxygen, O2:
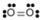
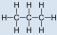
- Propane, C3H8:
Solution
- H2o is polar. Any molecule with lone pairs of electrons effectually the central cantlet is polar.
- Methanol is polar. This is non a symmetric molecule. The \(\ce{-OH}\) side is different from the other iii \(\ce{-H}\) sides.
- Hydrogen cyanide is polar. The molecule is not symmetric. The nitrogen and hydrogen accept different electronegativities, creating an uneven pull on the electrons.
- Oxygen is nonpolar. The molecule is symmetric. The two oxygen atoms pull on the electrons by exactly the same amount.
- Propane is nonpolar, because information technology is symmetric, with \(\ce{H}\) atoms bonded to every side around the central atoms and no unshared pairs of electrons.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{i}\)
Label each of the post-obit as polar or nonpolar.
a. SOthree
b. NH3
- Reply a
-
non polar
- Respond b
-
polar
Summary
- Non polar molecules are symmetric with no unshared electrons.
- Polar molecules are asymmetric, either containing lone pairs of electrons on a central cantlet or having atoms with different electronegativities bonded.
rollinsandelibubled.blogspot.com
Source: https://chem.libretexts.org/Courses/Sacramento_City_College/SCC%3A_CHEM_330_-_Adventures_in_Chemistry_(Alviar-Agnew)/04%3A_Chemical_Bonds/4.12%3A_Shapes_and_Properties-_Polar_and_Nonpolar_Molecules
0 Response to "How Do You Know if a Molecule Is Symmetrical"
Post a Comment